India-France Comprehensive Economic and Commercial Brief
(as per December 4, 2023)
Table of Contents
-
Overview of the French Economy
-
India-France Economic & Commercial Relations
3. Bilateral Agreements/Memorandum of Understanding (MoU)
4. India-France Business Associations in France
5. Activities for promoting Trade and Investment
6. Recent Ministerial Visits from India to France
1. Overview of the French Economy
France is ranked as the world’s seventh largest economic power, just behind the United Kingdom and India (WEF, 2022). After suffering one of the sharpest economic contractions among EU countries in 2020 (-8%) due to the COVID-19 pandemic, France’s economy recovered strongly in 2021 (+6.8%). However, Russia’s invasion of Ukraine and the subsequent energy crisis dampened the recovery by reducing consumers’ purchasing power, denting confidence, and exacerbating supply-side difficulties (IMF). Economic growth slowed down to 2.5% in 2022, and according to IMF forecasts, it should further decrease to 0.7% in 2023 before strengthening to 1.6% in 2024.
In 2022, after a strong economic recovery from the COVID-19 pandemic in 2021, France’s economy was hit by an energy crisis driven by Russia’s invasion of Ukraine. Despite its reliance on nuclear energy and low dependence on Russian gas, France faced a sharp slowdown in economic activity and high inflation. A strong policy response was put in place to tackle the crisis, equivalent to over 2% GDP, and including gas and electricity price freezes, cash transfers to households, a fuel price rebate, and support for enterprises (IMF). Budget deficit decreased from -5.1% GDP in 2021 to -4.5% GDP in 2022, but it is expected to remain high in 2023 (-4.8% GDP) before decreasing in 2024 (-4.3%) thanks to fiscal consolidation measures (IMF). Public debt, which is one of the highest in the euro zone, slightly decreased from 112.6% GDP in 2021 to 111.8% GDP in 2022. However, it is expected to rise again in 2023 (112.5% GDP) and 2024 (113.5% GDP). Driven by supply chain bottlenecks and the energy price shock, inflation soared from 2.1% in 2021 to 5.8% in 2022, but remained well below the EU average, largely due to energy price controls and subsidies (IMF).
YoY Annual Inflation Rate
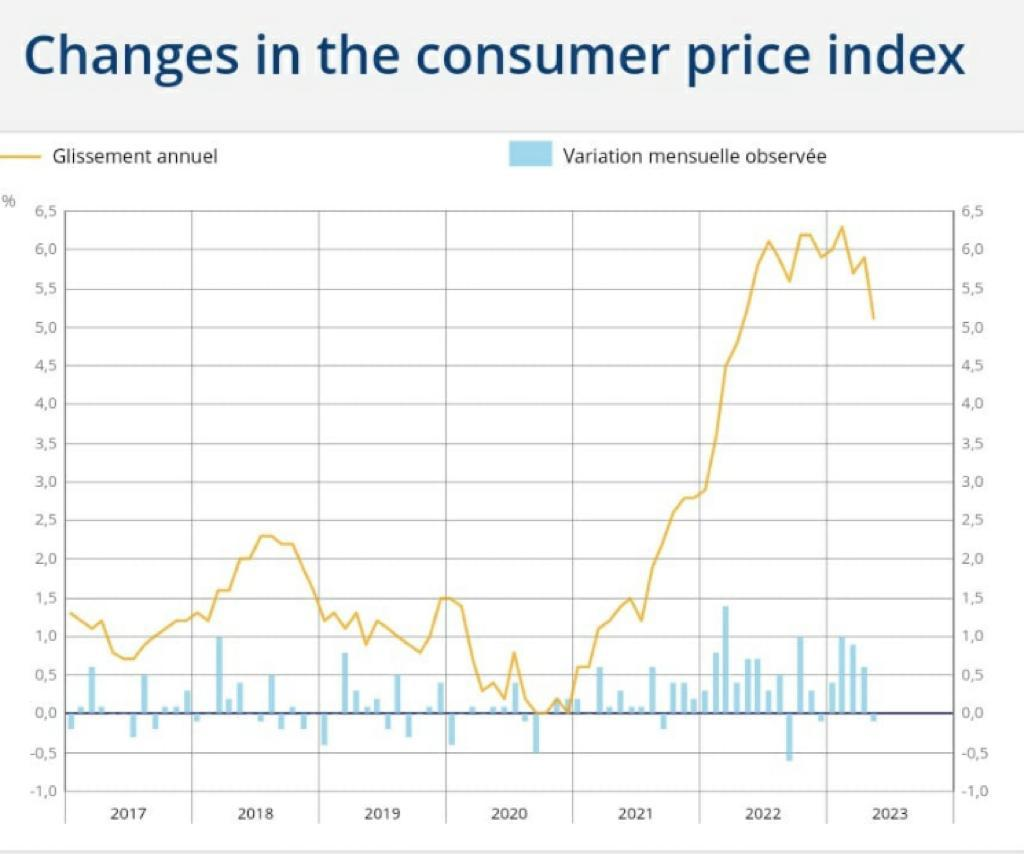
It is expected to remain high in 2023 (4.6%) before declining to 2.4% in 2024 (IMF). The priorities for 2023 include tackling inflation and protecting households, minimizing the rise in unemployment, accelerating ecological transition and supporting health care and education. The France 2030 Plan aims at boosting critical innovation and investment. In addition to the risk posed by new strains of the COVID-19 virus and waning vaccine effectiveness, France faces structural challenges: high structural unemployment, weak competitiveness, and high public and private debt burdens. High unemployment rates, especially among youth, remain a growing concern for policymakers.
Unemployment rate, which peaked at 8% in 2020, declined to 7.5% in 2022 and is expected to remain around that level in 2023 (7.6%) and 2024 (7.5%) (IMF). The deployment of short-time work scheme limited large-scale employment losses but continued efforts to boost worker skills and address inefficiencies in the educational system will be key (IMF). Social mobility remains low and the employment rates of many disadvantaged groups are poor.
The GDP per capita was USD 55,698 (€ 52,220) in 2022.
France is an important member of the G-7, OECD and G-20. Its technological strengths make it the leader in sectors such as aviation, space, food processing, transport, railways and agricultural research.
2. India-France Economic & Commercial Relations
The economic and commercial relations are an important component of India's bilateral relations with France. The economic relationship has been broadened over the years because of various factors including economic reforms process in India, thirteen Prime Ministerial visits from India to France in the period 1992-2023, the visit of our President to France in 2000, the visit of the French Prime Minister to India in 2003, seven visits of the French President to India in the period 1998-2018, and the growing French interest in establishing its presence in Indo-Pacific markets including in India. The series of high-level visits in the commercial and economic field reflects the growing interest of both the governments in expanding trade between the two countries. France considers India an important market for its products and is looking to increase the number of joint ventures and encouraging investments in and from India. Both countries are also moving to jointly develop technologies and integrate existing technologies. The process of enabling Unified Payment Interface is ongoing. Several Indian companies have opened their innovation centers in France for joint technology development including Tata Technology and L&T Tech Service. French technologies especially in renewables, sustainable manufacturing and urban infrastructure development are being integrated in India.
2.1 Bilateral Trade in Goods
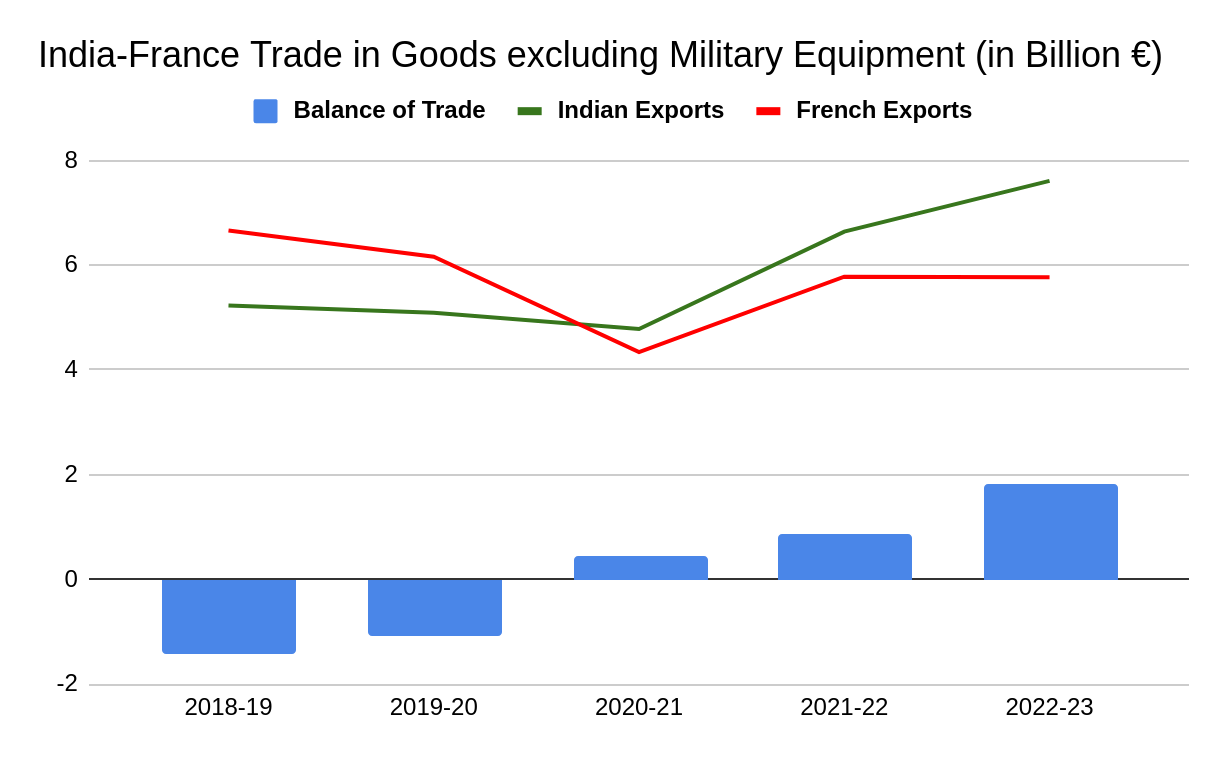
The bilateral trade between India and France have remained steady in between $11-13 bn. range in last 5 years ending FY 2022-23. The total trade for FY 2022-23 has breached the $13 bn. trade mark for the first time, with exports from India crossing $7 bn. India’s exports to France have steadily increased in last 5 years from $5.23 bn. in 2018-19 to $7.61 bn. in 2022-23. The Indian exports have shown an average growth of 45.5% over the period 2018-19 to 2022-23 with high variability on account of impact of COVID-19 pandemic. India’s imports from France, on other hand have decreased in the last 5 years from $6.66 bn. in 2018-19 to $5.77 bn. in 2022-23, thereby reversing the trade balance in the favor of India.
India-France Trade in Goods in the last 5 years (in Billion €)
|
Year
|
Indian Exports
to France
|
French Exports
to India
|
Total
Trade
|
Balance
of Trade
for India
|
Y-o-Y %
Changes
in Total Trade
|
|
2018-19
|
5.23
|
6.66
|
11.89
|
-1.43
|
+4.15
|
|
2019-20
|
5.09
|
6.16
|
11.26
|
-1.07
|
-5.29
|
|
2020-21
|
4.78
|
4.34
|
9.12
|
+0.44
|
-19
|
|
2021-22
|
6.64
|
5.78
|
12.42
|
+0.86
|
+36.18
|
|
2022-23
|
7.61
|
5.77
|
13.38
|
+1.84
|
+7.72
|
Source: Ministry of Commerce & Industry (Data rounded off to nearest billion €)
-
Top 5 Exports from India to France (FY 2022-23)
a) Mineral fuels, mineral oils & products of their distillation; bituminous substances; mineral waxes ($1.29 bn.)
b) Nuclear reactors, boilers, machinery & mechanical appliances; parts thereof ($974 mn.)
c) Electrical machinery and equipment & parts thereof; sound recorders & reproducers, television image and sound recorders and reproducers, and parts ($704 mn.)
d) Pharmaceutical products ($447 mn.)
e) Articles of apparel and clothing accessories, not knitted or crocheted ($390 mn.)
-
Top 5 Imports by India from France (FY 2022-23)
a) Aircraft, spacecraft, and parts thereof ($1.75 bn.)
b) Nuclear reactors, boilers, machinery & mechanical appliances; parts thereof ($933 mn.)
c) Electrical machinery and equipment & parts thereof; sound recorders & reproducers, television image and sound recorders and reproducers, and parts ($505 mn.)
d) Mineral fuels, mineral oils & products of their distillation; bituminous substances; mineral waxes ($410 mn.)
e) Optical, photographic cinematographic measuring, checking precision, medical or surgical instrument and apparatus parts and accessories thereof ($237 mn.)
Source: Ministry of Commerce & Industry
2.2. Bilateral Trade in Services
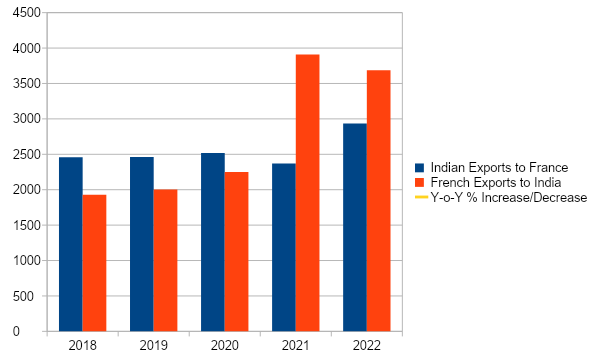
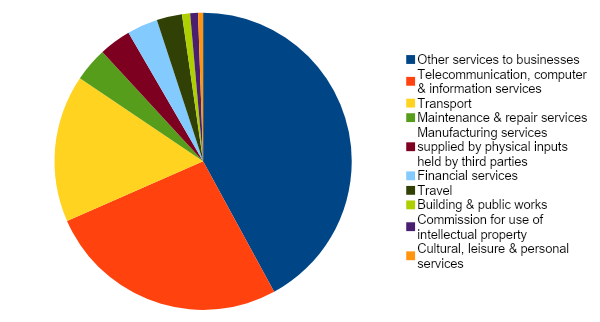
Based on annual data provided by the French Central Bank (Banque de France), the Indian exports of services to France from January to December 2022 registered an increase of 23.83% as compared to the same period of the previous year from € 2.37 billion to € 2.93 billion, with the following five categories of services recording a growth (in descending order):
-
Building & public works (+420%)
-
Travel (+72.34%)
-
Transport (+41.44%)
-
Other services to businesses (+34.20%)
-
Financial services (+16.66%)
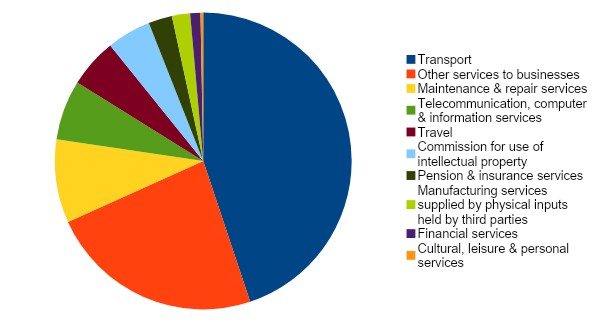
The Indian imports of services from France have recorded a decrease of 5.73% from € 3.90 billion in 2021 to € 3.68 billion in 2022, with however the following seven categories of services which contributed to a substantial growth (in descending order):
1) Building & public works (+200%)
2) Pension & insurance services (+177.86%)
3) Travel (+126.43%)
4) Financial services (+51.85%)
5) Transport (+37.78%)
6) Cultural, leisure & personal services (+37.50%)
7) Maintenance & repair services (+24.62%)
India-France Trade in Services over the last 5 Years (in Million €)
|
Year
(Jan.-Dec.)
|
Indian Exports
to France
|
French Exports
to India
|
Total
|
Y-o-Y% Increase/Decrease
|
|
2018
|
2,459
|
1,928
|
4,387
|
+1.97
|
|
2019
|
2,463
|
2,004
|
4,467
|
+1.82
|
|
2020
|
2,517
|
2,249
|
4,766
|
+6.69
|
|
2021
|
2,370
|
3,909
|
6,279
|
+31.74
|
|
2022
|
2,935
|
3,685
|
6,620
|
+5.43
|
Composition of India-France Trade in Services in 2022 (in Million €)
Composition of Indian Exports to France
Composition of French Exports to India
2.3 French Investments in India
2.3.1 France has emerged as a major source of FDI for India with more than 1,000 French establishments already present in India. France is the 11th largest foreign investor in India with a cumulative investment of USD 10.76 billion from April 2000 to September 2023 which represents 1.64% of the total FDI inflows into India according to data provided by the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT).
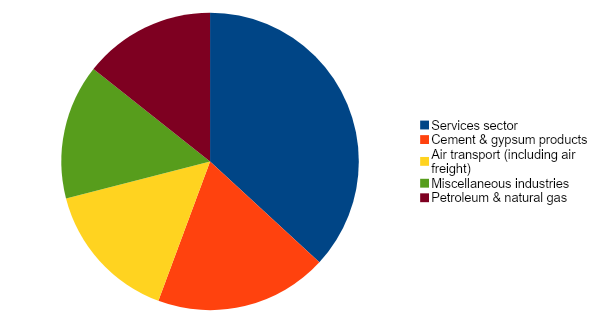
Top 5 FDI Equity Inflows from 2000-2023 are in:
1) Services sector (18.01%)
2) Cement & gypsum products (9.18%)
3) Air transport (including air freight) (7.50%)
4) Miscellaneous industries (7.16%)
5) Petroleum & natural gas (7.01%)
These five sectors represent 48.85% of the total equity inflow from France from 2000-2023.
2.3.2 Most big French groups have their subsidiaries in India. There are also a few joint ventures and liaison offices of French companies in India. 39 of the 40 CAC 40 (French Stock Market Index) companies are present in India. Around 50-70 SMEs are also present in India essentially in the mechanical and pharma-chemical sectors. French companies are present in a wide range of sectors: services (BNP Paribas, Capgemini, Havas, Sodexo); pharmaceutical-chemical (Arkema, L’Oréal, Sanofi, TotalEnergies); aerospace (Airbus, Dassault, Eurocopter, Safran, Thales); agro-food (Bongrain, Lactalis, Lesaffre, Pernod Ricard); electronics (Crouzet, Oberthur, Safran, STMicroelectronics, Thales); construction mechanics (Alstom, Cermex, Legris Group, Poclain, Sidel); electrical components (Hager, Legrand, Schneider Electric); automobile (Faurecia, Michelin, Plastic Omnium, Renault, Valeo).
2.3.3 French investments cleared in 2022 and 2023 include among others Worldline (transaction processing services), Systra (urban & rail transport engineering), Eutelsat (satellite connectivity services), Compagnie de Lanmeur (holding) and BNP Paribas (banking & financial services).
[According to the estimates from the Business France, public agency to promote trade, French companies employ around 300,000 persons in India and have a turnover of more than USD 20 billion and have a minimum stock investment portfolio of USD 19 billion].
FDI Equity Inflows from France from 2000-2023 (in Million €)
Source: DPIIT
2.4 Indian Investments in France
Indian businesses in France
2.4.1 Post-Brexit, several Indian businesses wanting to shift to mainland Europe are choosing France as their foremost place. There are more than 200 subsidiaries of Indian businesses established in France, employing 8,000 people, according to the ‘Business France Annual Report 2022’, a public operator supporting French investors in India and Indian investors in France.
2.4.2 The latest investments coming from India to France in 2021 and 2022 include:
-
Tata Technologies (2021), a product engineering and digital services company inaugurated an Innovation Center on December 6, 2022 to cater for the new-age product engineering and digital requirements in aerospace and defense sector. The investment will create 70 engineering jobs in coming two years.
-
Axiscades (2021), an engineering design company specializing in automotive, aerospace and defense engineering inaugurated their new facility in Montoir-de-Bretagne near Nantes (Pays de la Loire) on April 7, 2022 with the aim of creating 70 additional engineering jobs.
-
Aurobindo Group (2021)’s subsidiary Arrow Laboratories inaugurated its new facility in Ain near Lyon (Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes) in October 2021 with an investment of more than € 20 millions. The 7 hectares site has ultramodern facilities for value addition in generics and will create 100 jobs.
-
Electrosteel (2021), an Indian steel manufacturing company, inaugurated its new facility in Arles, near Marseille with plans to invest € 60 million in producing ductile iron pipes used predominantly in waterworks.
-
Tata Consultancy Services (2021), the French subsidiary of Tata Consultancy Services (TCS), a leader in the IT industry and digital transformation, has announced a new stage of development in Poitiers (Nouvelle-Aquitaine Region) with the inauguration of a service center. TCS has accelerated its job creation plan by setting itself the aim of recruiting 50 additional employees by the end of the first quarter of 2022, surpassing 100 employees at the site.
-
L&T Technology Services (2022) inaugurated its Engineering Design Center in Toulouse (Occitanie Region) on June 28, 2022 to cater end-to-end solutions for aerospace design and defense sector. The company plans to recruit 50 people within one year and around 100 people within three years for an investment of around € 2 million. The main idea for this Center in Toulouse is to serve the group’s customers in the aerospace industry, in France but also in Europe.
-
Pennar Group (2022), a multi-site and multi-product Indian mid-size company with a significant presence in the infrastructure, automotive, energy, engineering and construction sectors, has acquired a French company called Cadnum, based in Montluçon (Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes Region). The latter specializes in the design and manufacture of molds and special tools for the aerospace sector. This acquisition required an investment of € 2-3 million and enabled all jobs to be maintained. An additional recruitment of 10 to 15 people is envisaged over the next two years, with more investment of approximately € 1-1.5 million.
2.4.3 There were 13 investment decisions from India recorded in France in 2022, creating or maintaining 257 jobs, a 21% increase from 2021. Indian investments recorded in France in 2022 were split between R&D, engineering, design (6 projects; 79% of jobs), decision-making centers (4 projects; 12% of jobs), production/manufacturing activities (1 project; 6% of jobs), business services (1 project; 2% of jobs) as well as consumer services (1 project; 2% of jobs). Consulting and business services was the main sector concerned by Indian investments, including 5 projects out of the 13 identified in 2022 and nearly three quarters of all jobs (73%). Aerospace, naval and railway equipment came in second place, with 2 projects and 7% of jobs created or maintained.
2.4.4 Top 3 host French Regions (2022)
Location-wise, Indian businesses invested primarily in the Paris Region (capital: Paris), which received 7 projects and 25% of the resulting jobs, while the majority of jobs were created in Occitanie Region (capital: Toulouse) (51% of jobs through 2 projects) and Pays de la Loire Region (capital: Nantes) with 1 project.
2.4.5 France’s Position in Europe
In 2022, the leading European recipient of job-creating investment from India was the United Kingdom, followed by France and Germany.
2.4.6 Top 5 Indian Businesses by Employment in France (2022)
1. Tata Group (IT services & metalworking) (2,200 employees)
2. Biocon Biologics (biosimilars) (1,600)
3. Samvardhana Motherson Group (automotive) (1,500)
4. Centum Electronics (electrical & IT equipment) (575)
5. UPL (chemicals & plastics) (500)
As of December 31, 2021, the FDI stock in France was € 420 million (French Central Bank).
2.5 Issues related to Trade Protection/Rejection of Indian Goods, Sanitary and Phytosanitary/Technical Barriers and other Non-Tariff Barriers
2.5.1 The major issues for agricultural products that were highlighted in 2022 are as below:
a) Spices: EU in December 2021 applied new levels of minimum residue levels (MRL) for ethylene oxide which disqualifies large proportion of spices coming from tropical countries. Ethylene oxide synthesizes naturally in plants. The level of natural ethylene oxide is higher is tropical countries on account of higher metabolism due to high temperatures and moisture levels.
b) Basmati rice: It is not being recognized as GI product at the level of EU. Informally, the biggest rice importer of Europe shared that the rice association of France influenced the French Ministry of Agriculture to oppose the recognition of Basmati Rice as GI product.
2.6 Bilateral Mechanisms to promote Trade and Investments
2.6.1 India-France Joint Committee for Economic & Technical Cooperation (JCETC) was set up on January 26, 1976 through an exchange of letters between the Ministers of Commerce and Foreign Trade. Meetings are held at Ministerial level alternately in Delhi and Paris. This Joint Committee is the major institutional mechanism for cooperation in the economic and technical sector. The 17th session of the Joint Committee was held on October 24, 2017 in Paris. The entire gamut of bilateral economic and commercial relationship was reviewed at the meeting, and both sides agreed to continue and intensify cooperation. The 18th session of the India-France Joint Consultative Meeting (JCM) was held virtually on November 27, 2020. A joint announcement was also signed for setting up of a Fast-Track system for French companies in India and Indian companies in France which was to be made operational by the end of December 2020.
2.6.2 Joint Working Groups (JWGs) at the senior official level have also been constituted through MoUs to deal with specific aspects of economic cooperation, including for Agriculture and Food Processing, IT & Telecommunications, Roads, Sustainable Urban Development and Energy. During the visit of French President to India (14-15 February, 2013), the two countries further agreed to establish an annual bilateral Economic and Financial Dialogue (EFD) between the two Finance Ministries on economic and financial issues.
The status of different JWGs is as follows:
a) The first such Economic and Financial Dialogue was held in Paris on October 29, 2013. No meeting post this took place.
b) The 3rd JWG on Environment was held on 18-19 January, 2021 in New Delhi.
c) The 15th JWG Meeting on Sustainable Urban Development was held virtually on 2-3 March, 2021. The 16th JWG on Sustainable Urban Development took place on 16 January, 2023 in New Delhi.
d) The 9th JWG meeting on Agriculture including Food Processing was scheduled to take place virtually on March 25, 2021 but has been postponed. The 8th JWG on Agriculture including Food Processing was held on 6-7 December, 2016 in Paris.
3. Bilateral Agreements/Memorandum of Understanding (MoU)
3.1 India and France have signed a number of Agreements to facilitate the expansion of commercial relations.
3.2 Among these are the Double Taxation Avoidance Convention (DTAC) [where India has requested a protocol, to amend Article 28 to insert new disclosure norms on which bilateral consultations are continuing], MoU on cooperation in Tourism, MoU on Intellectual Property and a Social Security Exemption Agreement (SSA).
3.3 In October 2012, India and France signed an Agreement for cooperation in the field of Sustainable Urban Development. Another MoU on Bilateral Cooperation in Food Industries Sector was signed on October 24, 2012.
3.4 During the visit of French President to India (14-15 February 2013), the two countries concluded an MoU between the Ministry of Railways of the Republic of India and the French National Railways (SNCF) on Technical Cooperation in the field of Railway Sector as well as a General Framework Agreement between Oséo (the French Innovation Promotion Agency) and Technology Development Board (TDB) of India to establish a collaborative framework under which Oséo and TDB may carry out activities related to the exchanging of best practices and the setting up of coordinated measures to foster technological exchanges and innovation collaborations between companies, organizations and institutions of France and India.
3.5 The following four agreements/MoUs were signed during the visit of Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi to France on 10-11 April, 2015:
-
MoU on cooperation in the field of renewable energy between the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE), Government of India and the Ministry of Ecology, Sustainable Development and Energy, Government of France;
-
Railway Protocol between Indian Ministry of Railways and French National Railways (SNCF) on cooperation in semi high speed rail and station renovation;
-
MoU between National Skill Development Agency (NSDA), India and the National Commission for Vocational Qualifications (Commission Nationale de la Certification Professionnelle - CNCD);
-
Letter of Intent on Tourism
3.6 During French President François Hollande’s visit to Indian in January 2016, MoUs were signed in the presence of Prime Minister Narendra Modi and Mr. Hollande in the field of smart and sustainable cities and helicopter production as also JV agreements and Letters of Intent in the field of renewable energy/wind energy.
India and France signed a MoU on civil aviation in April 2017 in New Delhi in the presence of Shri P. Ashok Gajapathi Raju, Minister of Civil Aviation, and Mr. Alain Vidalies, Minister of State for Transport, Marine Affairs and Fisheries, to strengthen India-France cooperation on transport.
3.7 Both countries signed a pact in March 2018 in New Delhi to deepen cooperation in the environment field while affirming their commitment to lead the fight against climate change. The pact was signed by the Minister of State for Environment, Shri Mahesh Sharma, and the French Minister of State, attached to the Minister for the Ecological and Inclusive Transition, Ms. Brune Poirson.
3.7 The following four MoUs were signed during the visit of Prime Minister, Shri Narendra Modi, to France in August 2019: i) MoU between the National Institute of Solar Energy (NISE), Ministry of New and Renewable Energy, and the French Alternative Energies and Atomic Energy Commission (CEA),
ii) Administrative arrangement between the Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship, and the French Ministry of National Education and Youth, for Cooperation in Skill Development and Vocational Training,
iii) Cooperation agreement between the Centre for Development of Advanced Computing (C-DAC), an autonomous scientific society of the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology and Atos, a French multinational IT service and consulting firm & iv) Implementing arrangement between ISRO and CNES (France) for Joint Maritime Domain Awareness.
3.8 The partnership agreement for migration and mobility signed on March 10, 2018 between France and India came into effect into force in October 2021. This France-India partnership is a positive response to the labor shortage in certain fields of activity in France. This agreement is part of the development of cooperation on free movement of people and the fight against illegal immigration and should boost mobility from India to France. Mission organized an event to promote and discuss the Migration and Mobility Partnership Agreement in partnership with CII. About 75 partners including professionals, recruitment agencies, companies based in France on November 26, 2022.
3.9 Agreement on Social Security
An Agreement on Social Security exemption was signed during Prime Minister’s visit in September 2008. The Agreement has been ratified by the two sides and has come into force on July 1, 2011. The agreement will protect the interests of expatriate workers and the companies on a reciprocal basis. It helps workers by (i) providing for exemption from social security contribution in case of short-term contracts; (ii) exportability of pension in case of relocation to the home country or any third country; and (iii) totalization of the contribution periods.
3.10 VIE (Volontariat International en Enterprise)
Voluntary International Apprenticeship Program: Under this scheme, started in 2008, young French interns/graduates are sent to French companies in India as trainees for a period of one year. The cost is borne by the company utilizing the trainee, with Government defraying certain costs and offering tax subsidies to companies utilizing the scheme. At present there is a cap of 250 visas per annum under the scheme.
3.11 Indo-French CEO’s Forum
3.11.1 During French President, Mr. Nicolas Sarkozy,’s visit to India in January 2008, it was decided to establish an India-France Foundation which could begin as an India-France High Level CEO’s Round Table. The Indian side is headed by Mr. Hari Shankar Bhartia, Founder & Co-Chairman, Jubilant Bhartia Group (earlier by Mr. Dhruv Sawhney, Chairman, Triveni Engineering & Industries, and Mr. Narayana Murthy, Chief Mentor of Infosys). The French side is headed by Mr. Paul Hermelin, Chairman of the Board of Directors, Capgemini, and Special Representative of the French Government for Indo-French Economic Relations.
3.11.2 As of date, 11 meetings of CEO’s Round Tables have taken place, alternatively in New Delhi and Paris. The 1st meeting of the Forum was held on 28-29 November, 2009 in New Delhi. Over the years, the Indo-French CEO’s Forum has brought out its recommendations with relation to the Private-Public Partnerships, Corporate Social Responsibility, Sustainable Development, Education, Employability and Skill Development.
3.11.3 The 10th Indo-French CEO’s Forum was held on March 10, 2018 in New Delhi during President Macron’s official visit to India. The 11th Indo-French CEO’s Forum took place on July 14, 2023 in Paris on the occasion of the official visit of Prime Minister Modi. It was co-chaired by Mr. Hari Shankar Bhartia, Founder & Co-Chairman, Jubilant Bhartia Group and Mr. Paul Hermelin, Chairman of the Board of Directors, Capgemini.
3.12 India-France Economic Cooperation through AFD (French Agency for Development)
Pursuant to signing of a MoU in September 2008 between Department of Economic Affairs (DEA) and the French Agency for Development, the AFD extends credit for various projects in India. The priority areas for AFD economic cooperation in India are (i) energy efficiency and renewable energy within the framework of the National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC), (ii) urban infrastructure (public transport, water, etc., through sustainable development projects and infrastructure development programmes such as JNNURM), and (iii) the preservation of biodiversity. The current projects being supported by the AFD include (i) ‘Reorganizing the Water Supply System of Jodhpur City in Rajasthan’, Phase II worth € 71.1 million (ii) ‘Forestry and Bio-diversity Conservation Project in Assam’ worth € 54 million (iii) Credit Facility Agreement (CFA) for the Bangalore Metro Rail Project, Phase-I (iv) IREDA II and (v) Cochin Metro Project.
4. India-France Business Associations in France
a) France-India Chamber of Commerce and Industry (CCIFI, Boulogne-Billancourt) was created in 1984 as a non-profit organization that aims to promote bilateral commercial relations between India and France. It has as its members several Indian and French companies. The Mission has been working with CCIFI to promote bilateral relations through joint activities. The Chamber brings out a monthly newsletter in English which provides information in brief on various topics pertaining to economy, trade and industry.
b) With the support of the Mission, a France-India Business Club (Business Club France-Inde) was started in January 2014 in Marseille, the second largest city in France after Paris and the largest port, to assist Indian businesses, entrepreneurs and to generate interest about India among the French businesses in the Provence-Alpes-Côte d’Azur Region.
5. Activities for promoting Trade and Investment
5.1 Promotion of economic and commercial relations between India and France is a major priority for the Mission and the E&C Wing. The Mission works to promote Indian business and industry by encouraging trade and investment, assisting Indian firms with Government and private sector contacts, providing information, supporting and advising Indian companies about the French market.
5.2 Major commercial activities of the Mission include: (i) promotion of Indian goods and services in France, (ii) promotion of Brand India and corporate image of India, (iii) promotion of India as a foreign direct investment destination, and (iv) promotion of the ‘Make in India’ campaign. In each of these activities Mission’s action mostly involve gathering and dissemination of information, outreach, coordination and facilitation. Some of the recent events include:
-
Visit to France of a 20-member delegation comprising leading industry players from Gujarat led by Mr. Hareet Shukla, Secretary (Tourism), Government of Gujarat, to promote the 10th ‘Vibrant Gujarat Global Summit 2024’ to be held from 10-12 January, 2024 in Gandhinagar. The delegates met French companies and potential investors in order to present the attractiveness of doing business and investing in the State of Gujarat.
-
Shri Piyush Goyal, Minister of Commerce & Industry, Consumer Affairs, Food & Public Distribution and Textiles, visited Paris from 10-12 April, 2023 for various events on the occasion of the celebration of 25 years of India-France Strategic Partnership including the ‘India-France Business Summit’ organized by the Mission and a round table luncheon meeting of CEOs from both India and France co-chaired by CIM, Shri Piyush Goyal, and the Minister Delegate for Foreign Trade, Economic Attractiveness and French Nationals Abroad, Mr. Olivier Becht, on 11 April, 2023 in Paris. More than 50 CEOs from Indian and French companies participated in the CEO’s round table. The Minister was accompanied by a CII delegation of 15 CEOs headed by Vice-President of CII and Chairman & Managing Director of ITC Limited, Mr. Sanjiv Puri.
-
A round table luncheon meeting of CEOs from both India and France co-chaired by CIM, Shri Piyush Goyal, and the Minister Delegate for Foreign Trade, Economic Attractiveness and French Nationals Abroad, Mr. Olivier Becht, on 11 April, 2023 in Paris. More than 50 CEOs from Indian and French companies participated in the CEO’ s round table.
-
A mentorship event for the young Indian professionals by Indian professionals in senior positions in France, organized on February 11, 2023. Almost 50 young professionals and 20 senior professionals participated.
-
A networking event for senior professionals on January 17, 2023.
-
An event on Migration and Mobility Partnership Agreement in partnership with CII including professionals, recruitment agencies, companies based in France on November 26, 2022.
-
An event on Doing Business in India with National Chambers of France, MEDEF International and the bilateral chamber IFCCI on October 23, 2022 on the theme ‘Doing Business in India’. 25 French companies and lawyers participated in this.
-
An event on promoting trade and tourism between India and France was organized in Marseille on September 29, 2022. Almost 100 participants from the local government, companies based in the PACA Region and from diplomatic missions participated.
-
Two consecutive events to promote ‘Incredible India’ followed by an event to promote tourism in the State of Madhya Pradesh were organized on September 21, 2022. Almost 70 persons including tour operators, social media influencers, people from public relations and local chambers participated in the event.
6. Recent Ministerial Visits from India to France
6.1 The Union Defence Minister, Shri Rajnath Singh, met with the CEOs of the top French defence companies (Mr. Eric Trappier, CEO, Dassault; Mr. Pierre-Eric Pommellet, CEO, Naval Group; Mr. Guillaume Faury, CEO, Airbus & Mr. Olivier Andriès, CEO, Safran) on 10-11 October, 2023 in Paris. The Union Minister also visited the Safran Engine Division's R&D Centre in Gennevilliers and also participated at the 5th Annual Defence Dialogue with the French Minister of Armed Forces, Mr. Sébastien Lecornu.
6.2 Participation of Smt. Nirmala Sitharamn, Minister of Finance and Corporate Affairs, at the ‘Summit for a New Global Financial Pact’ organized by the French Presidency on 22-23 June, 2023 in Paris.
6.3 Shri Bhupender Yadav, Minister of Environment Forest and Climate Change, visited France on 26-27 May, 2023 to participate at the High Level Sequence (HLS) and High Level Event (HLE) organized by the Government of France at UNESCO prior to the Second Meeting of the Inter Governmental Negotiating Committee to develop an International Legally Binding Instrument on Plastic Pollution.
6.4 Dr. L. Murugan, Minister for Fisheries, Animal Husbandry and Dairying & Information and Broadcasting, visited France to take part at the 76th Annual Cannes Film Festival from 16-18 May, 2023 and to visit a Fish Auction in Boulogne-sur-Mer on 20 May, 2023.
6.5 Shri Piyush Goyal, Minister of Commerce & Industry, Consumer Affairs, Food & Public Distribution and Textiles, visited Paris from 10-12 April, 2023 for various events on the occasion of the celebration of 25 years of India-France Strategic Partnership including The India-France Business Summit organized by the Mission and a round table luncheon meeting of CEOs from both India and France co-chaired by CIM, Shri Piyush Goyal, and the Minister Delegate for Foreign Trade, Economic Attractiveness and French Nationals Abroad, Mr. Olivier Becht on 11 April, 2023 in Paris. More than 50 CEOs from Indian and French companies participated in the CEO’s Round Table. Hon’ble Minister also held one to one meetings with Secretary General of the OECD, Director General of the International Energy Agency, CEOs of Danone, Roquette, Capgemini and BNP Paribas among others. The Minister was accompanied by a CII delegation of 15 CEOs headed by Vice-President of CII and Chairman & Managing Director of ITC Limited, Mr. Sanjiv Puri.
6.6 Shri Ashwini Vaishnaw, Minister of Communications and Electronics & Information Technology and Railways, inaugurated the India Pavilion at the 6th Annual Technology Conference, ‘Viva Technology’, on 15 June, 2022 where India was the ‘Country of the Year’. The Indian delegation comprised over 100 CEOs and Digital Experts, 66 start-ups of which 15 were present at the India Pavilion at Porte de Versailles (Paris).
6.7 An Indian delegation led by Shri Anurag Singh Thakur, Minister of Information & Broadcasting, and Dr. L. Murugan, Minister of State of Information & Broadcasting, Fisheries, Animal Husbandry and Dairying, visited Cannes for the Annual Cannes Film Festival Market organized from 17-25 May, 2022 where India was the ‘Country of Honor’. CII organized an India Pavilion at the festival. Mr. Abhay Kumar Sinha, Director General, Services Export Promotion Council, & Mr. Hirachand Damji Dand, Entertainment Committee Chairman, participated at the event to promote exports of 17 services sectors.
6.8 Shri Mansukh Mandaviya, Union Minister of Health & Family Welfare and Chemicals & Fertilizers, visited Evian-les-Bains from 6-7 April, 2022 for the Gavi Alliance Board Retreat Conference to discuss the vaccine sharing protocol for the countries of South.
6.9 External Affairs Minister, Dr. S. Jaishankar, attended the EU Ministerial Forum for Indo-Pacific Cooperation on February 22, 2022 in Paris, an initiative of the French Presidency of the European Council. He also had a meeting with his French counterpart, Mr. Jean-Yves Le Drian. He also presided the meeting of Indian Ambassadors in the EU on February 23, 2022 in Paris.
6.10 Apart from these visits, there were regular visits by Ministers from five States of Uttar Pradesh (December 2022), Karnataka (October 2022), Haryana (October 2022), Madhya Pradesh (September 2022) and Kerala (September 2022) to promote trade, tourism and technology ties between France and the respective State.
*****